- HOME
- Workflow automation
- What is workflow management? A complete guide
What is workflow management? A complete guide
- Last Updated: March 30, 2024
- 611 Views
- 15 Min Read

A workflow is a defined sequence of tasks, actions, or steps required to accomplish a specific goal within a routine business process. It outlines the systematic flow of activities from initiation to completion, ensuring efficient allocation of resources and timely execution.
Mastering workflow management in the initial phases of business development is essential for any organization, regardless of scale. This involves optimizing processes, assigning tasks efficiently, and fostering clear communication among team members. Automating aspects of workflow management can significantly improve productivity and streamline operations. Additionally, promoting a culture of collaboration and adaptability within your team is equally important to ensure seamless operations and achieve optimal results.
By effectively utilizing automation tools and nurturing a collaborative team culture, you can optimize streamlined workflows and set your business process management on the path to long-term growth.
What is workflow management?
Workflow management refers to the coordination and automation of tasks, processes, and activities within an organization to ensure smooth and efficient operations. This helps to design, execute, and optimize workflows, achieving specific objectives and improving productivity.
The strength of workflow and project management lies in its ability to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, minimize errors, and increase overall productivity. Organizations can better allocate resources, reduce costs, and deliver higher-quality products or services promptly by applying an effective workflow by applying an effective workflow.
Understanding workflow management
At its core, workflow management focuses on the systematic coordination and optimization of tasks and activities required to achieve specific objectives or complete processes within an organization. In a structured manner, various basic components such as inputs, outputs, triggers, tasks, and resources are defined to ensure efficient execution.
Workflow management systems facilitate the design, monitoring, and automation of workflows, thereby streamlining operations and enhancing productivity.
Components of workflow management
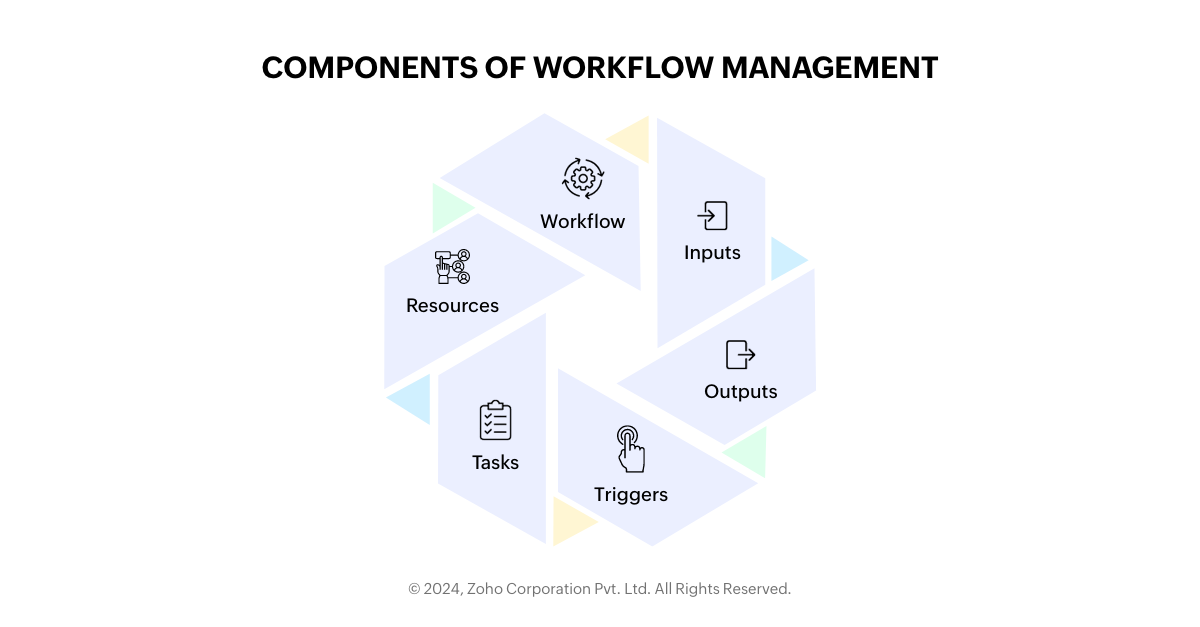
1. Workflow
In business process management, a workflow serves as a structured pathway that guides the progression of tasks and activities toward achieving a specific objective. It ensures clarity and efficiency in how you conduct work by outlining the sequence of steps or actions required.
Workflows streamline processes and enhance productivity within the organization by defining the order in which tasks are completed and the relationships between them to optimize efficiency. By minimizing unnecessary steps and reducing bottlenecks, optimized workflows enable organizations to achieve their goals more quickly and with greater precision.
2. Inputs
Inputs encompass the data, information, or resources that are necessary to initiate and support the execution of tasks within a workflow. These inputs form the foundation for building tasks and guide decision-making throughout the process.
Whether it is raw materials, customer information, or project specifications, identifying and managing inputs effectively is essential for ensuring that workflows operate smoothly and efficiently.
3. Outputs
Outputs represent the tangible or intangible outcomes generated due to completing tasks within a workflow. They can take various forms, including products, services, reports, or insights. The outputs of a workflow reflect its progress and efficacy by signaling the completion of tasks and the realization of its goals.
However, it's essential to recognize that outputs can sometimes deviate from expectations or be inaccurate, requiring continuous monitoring and adjustments to ensure desired correct outcomes.
4. Triggers
Triggers are the stimuli or events that initiate or influence the execution of specific tasks within a workflow. They act as catalysts for action, prompting individuals or systems to respond accordingly. Predefined conditions, like reaching a particular deadline or receiving a customer inquiry, can trigger a response, or external factors may require a proactive response.
By identifying and effectively managing triggers, organizations can ensure timely and appropriate task execution within their workflows.
5. Tasks
The workflow requires individuals to perform specific actions or steps, known as tasks, to achieve the desired outcome. They are the operational units of work within the process, each contributing towards the overall goal.
Tasks can vary in complexity and duration, requiring different resources and skills for completion. Properly defining, assigning, and sequencing tasks plays an essential role in maintaining workflow efficiency and ensuring that we meet the objectives within the specified timeframe.
6. Resources
Resources encompass the people, workflow management tools, equipment, or assets that are utilized in the execution of tasks within a workflow. They provide the necessary support and capabilities to conduct work effectively and efficiently. Managing resources involves identifying needs, allocating appropriate assets, and optimizing utilization to maximize productivity.
Whether it is skilled personnel, specialized software, or physical infrastructure, using resources effectively is essential for achieving optimal workflow performance and delivering desired outcomes.
Types of workflows
Workflows, the backbone of organizational processes, span diverse types. Each type offers a structured approach, enhancing efficiency and meeting organizational goals seamlessly.
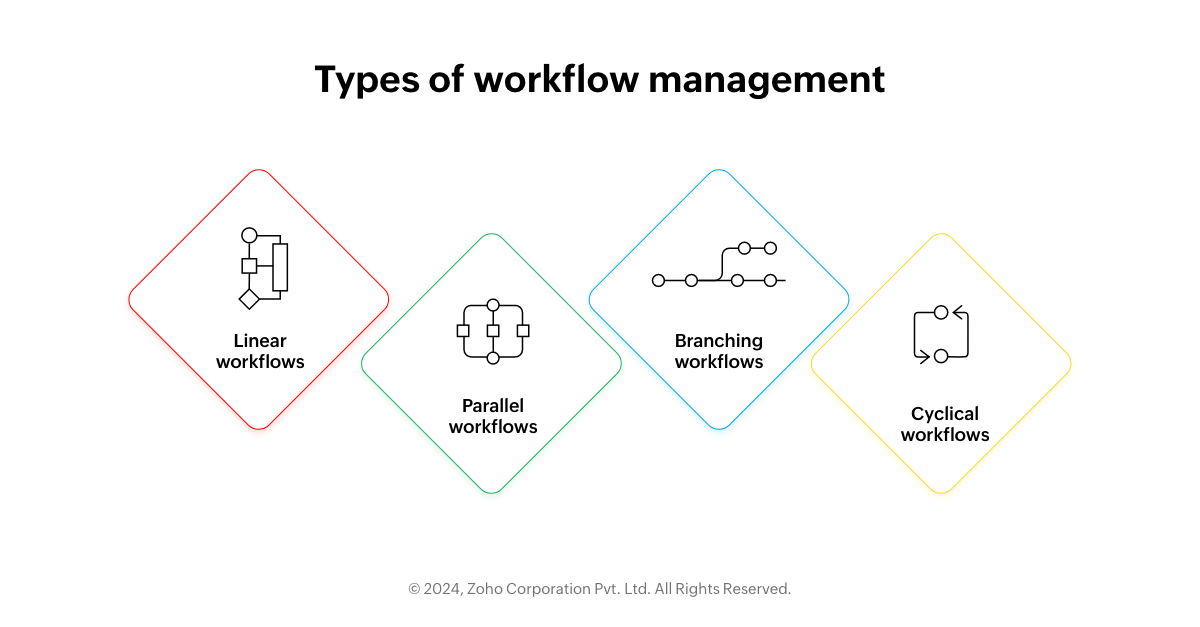
Linear workflows
Linear workflows, also referred to as sequential workflows, follow a clear and linear progression from one task to the next.
Each step in the workflow is dependent on the successful completion of the preceding task.
This structured approach ensures that tasks are performed in a specific order, typically following a predefined sequence.
Sequential workflows are commonly used in processes where tasks have a strict dependency on one another and where there is a clear start and end point.
Examples include manufacturing assembly lines, document approval processes, and software development methodologies like waterfall, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next.
Parallel workflows
Parallel workflow, also referred to as concurrent workflow, involves the simultaneous execution of multiple tasks or activities.
Unlike linear workflows, where tasks are completed in a sequential path, concurrent workflows enable different tasks to be performed concurrently.
This parallel processing can significantly reduce the overall time required to create workflows.
Concurrent workflows are particularly beneficial in scenarios where tasks are independent of each other and can be executed in parallel without any dependencies.
Common examples include large-scale data processing, where data can be analyzed, transformed, and aggregated concurrently across multiple nodes or processors, thereby accelerating the analysis process.
Branching workflows
Branching workflows encompass multiple paths or branches, where the sequence of tasks followed varies based on specific conditions or decisions encountered during workflow execution.
All these workflows incorporate decision points or conditional branching, where the workflow diverges into different paths based on the evaluation of specific criteria or variables.
Each branch may lead to different sets of tasks or actions being executed, depending on the outcome of the decision.
Branching workflows are flexible and adaptable, allowing for dynamic routing and accommodating varying scenarios or inputs.
They are commonly used in processes involving decision-making or multiple possible outcomes, such as approval workflows with different approval levels or customer service processes with varying paths of resolution based on customer inquiries.
Cyclical workflows
Cyclical workflows, also known as iterative or repetitive workflows, involve the execution of repetitive tasks or activities in a cyclical manner.
Unlike linear workflows with a clear start and end point, cyclical workflows loop back to earlier stages after completing a cycle, allowing for continuous improvement or refinement of the workflow process.
These workflows are prevalent in agile development methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban. In these workflows, tasks are executed in successive cycles or iterations, with each cycle building upon the outcomes of the previous one.
Cyclical workflows are ideal for processes that require ongoing optimization, feedback incorporation, or continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing requirements or feedback loops effectively.
Examples include software development processes, quality assurance procedures, and product refinement cycles in manufacturing.
The need for workflow management
Understanding the various types of workflows is essential for realizing the significance of a workflow management system. By grasping different workflow structures and processes, businesses can implement strategies to enhance productivity, streamline operations, and achieve organizational objectives effectively. The necessity for workflow management becomes apparent in facilitating efficient business operations. These are some of the needs for the best workflow management:
1. Efficiency improvement
Workflow management system enables organizations to streamline their processes by automating repetitive tasks, eliminating bottlenecks, and optimizing resource allocation.
By standardizing workflows and defining clear procedures, organizations can reduce unnecessary steps and improve the overall efficiency of task execution. The continuous monitoring and analysis of workflows allow organizations to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance efficiency over time.
2. Resource allocation
Workflow management helps organizations allocate resources effectively by aligning them with the demands of different tasks and processes. Through workflow analysis, organizations can identify resource-intensive tasks or processes and reallocate resources accordingly to ensure optimal utilization.
By automating resource allocation processes, such as task assignment and scheduling, workflow management systems help minimize resource wastage and improve overall productivity.
3. Consistency
Consistency in task execution is essential for maintaining quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction. A workflow management system ensures consistency by standardizing procedures, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and enforcing adherence to established workflows.
By providing guidelines, templates, and automated workflows, organizations can ensure that tasks are performed consistently across different teams and departments.
4. Standardization
The standardization of workflows is essential for ensuring uniformity, compliance, and scalability across the organization. A workflow management system facilitates standardization by documenting and formalizing processes, procedures, and best practices.
Standardized workflows enable organizations to achieve greater efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance accessibility by providing clear guidelines and structured processes to follow, thereby ensuring consistent performance across teams and achieving business objectives.
5. Visibility
Visibility into workflow processes allows stakeholders to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. The workflow management system provides real-time visibility into task status, dependencies, and performance metrics through interactive dashboards, reporting features, and notifications. This enables stakeholders to monitor the flow of work, identify potential issues promptly, and take necessary actions to ensure efficient operations and timely project completion.
Increased visibility enables proactive problem-solving, resource optimization, and better alignment of workflows with organizational goals and priorities. By granting granular control over workflows, increased visibility allows stakeholders to identify specific tasks, the individuals responsible for their completion, and the methods used to accomplish them. This level of insight enables organizations to pinpoint areas for improvement, allocate resources more effectively, and ensure that workflows are aligned with strategic objectives.
6. Transparency
Transparency promotes accountability, trust, and collaboration within the organization. A workflow management system enables transparent communication, documentation, and tracking of task assignments, deadlines, and outcomes through centralized dashboards accessible to all stakeholders. This allows for clear visibility into task progress, responsibilities, and results, fostering open communication channels and ensuring that everyone is informed and aligned with organizational objectives.
Additionally, by providing a historical record of actions taken and decisions made, the system facilitates accountability and supports continuous improvement efforts. Transparent workflows empower employees to take ownership of their tasks, collaborate more effectively with team members, and contribute to overall organizational success.
7. Compliance
Compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies is critical for avoiding legal and reputational risks. This helps organizations establish and enforce compliance measures by incorporating regulatory requirements into workflow design and execution.
By integrating compliance checks, approvals, and documentation into workflow processes, organizations can ensure adherence to standards and mitigate compliance-related risks.
8. Governance
Governance of workflow processes ensures alignment with organizational objectives, policies, and strategic priorities. A workflow management system facilitates seamless governance by providing comprehensive mechanisms for oversight, control, and decision-making.
Effective governance ensures that organizations design, execute, and monitor workflows according to established guidelines, standards, and governance frameworks to support their goals and objectives.
Addressing business challenges
Effective workflow management addresses various challenges that organizations encounter in their day-to-day operations. These challenges include disorganization, bottlenecks, delays, and errors, which can significantly impede productivity, hinder progress, and increase costs.
1. Disorganization
When workflows lack proper management, they risk becoming chaotic and disordered, causing confusion and inefficiency among team members. This absence of structure hampers productivity and can impede progress within the organization.
2. Bottlenecks
Within workflows, bottlenecks represent points where tasks encounter obstacles or slowdowns, often due to resource limitations or inefficiencies in task execution. These bottlenecks disrupt the smooth flow of work, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
3. Delays
Inefficient workflows often result in delays in task completion, leading to missed deadlines and jeopardizing project timelines. These delays not only affect productivity but also impact the overall success of projects and initiatives.
4. Errors
Manual processes and miscommunication within workflows can contribute to errors or inaccuracies in task execution. These errors undermine the quality and reliability of outcomes, leading to rework, customer dissatisfaction, and increased costs for the organization.
Impact
Inefficient workflow management can significantly harm organizational performance, hinder productivity and progress, and lead to unnecessary expenses. This presents formidable obstacles to meeting organizational goals and staying competitive in the market.
1. Decreased productivity
When workflow management is ineffective, it leads to inefficient processes that consume valuable time and resources without producing optimal results. This inefficiency diminishes the overall productivity of the organization, as tasks take longer to complete and require more effort than necessary.
Consequently, employees may feel overwhelmed or demotivated, and the organization may struggle to achieve its goals efficiently.
2. Missed deadlines
Ineffectiveness often leads to delays in task completion, causing deadlines to be missed. These missed deadlines can have detrimental effects on project timelines and stakeholder expectations.
Clients may lose confidence in the organization's ability to deliver on time, damaging relationships and leading to lost opportunities or contracts. Moreover, missed deadlines can tarnish the organization's reputation and credibility in the industry.
3. Increased costs
Inefficient workflows are costly, as they waste resources and require additional time and effort to rectify errors or delays. These inefficiencies contribute to higher operational costs, including expenses associated with wasted resources, overtime pay, and potential penalties for failing to meet contractual obligations.
Moreover, the need for rework or corrective actions to address poor-quality outcomes further escalates costs, straining the organization's financial resources and hindering its competitiveness in the market.
Benefits of workflow management
Implementing a robust workflow management system offers several advantages to organizations, helping them streamline processes, improve collaboration, and enhance transparency and accountability.
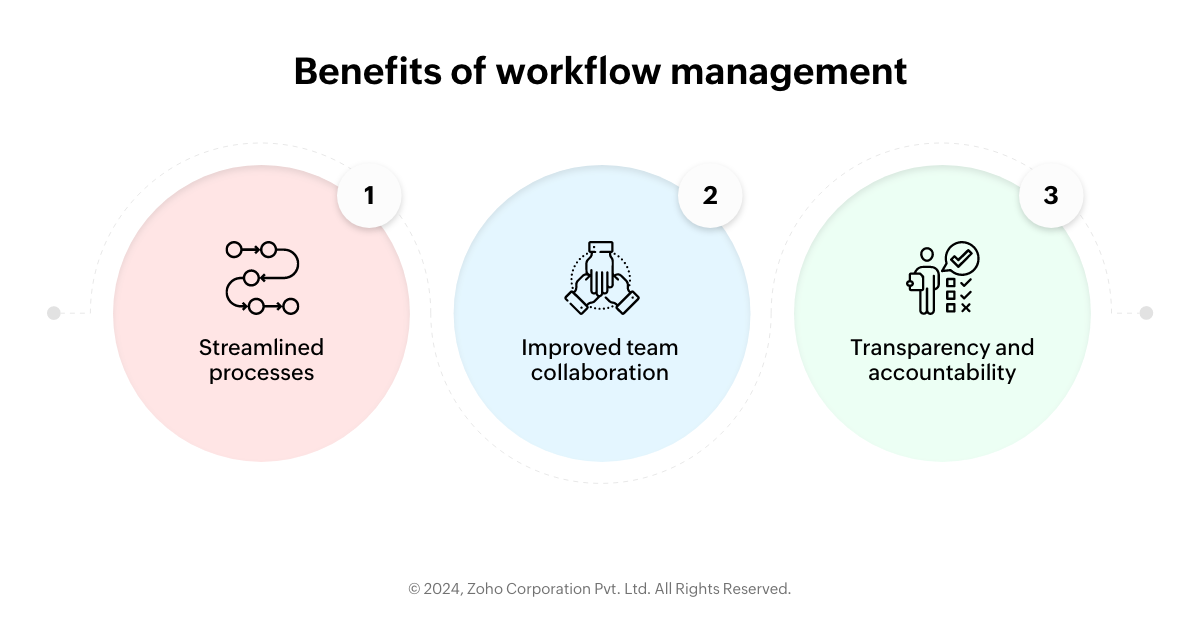
1. Streamlined processes
Efficient workflow management eliminates redundancies, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies, resulting in smoother, more streamlined processes. By optimizing task sequences and resource allocation, organizations can achieve higher levels of operational efficiency and productivity.
2. Improved team collaboration
Effective workflow management fosters better communication, coordination, and collaboration among team members. By providing visibility into task assignments, status updates, and dependencies, this system enables teams to work together more effectively, leading to enhanced teamwork and synergy.
3. Transparency and accountability
A workflow management system provides clear visibility into tasks, responsibilities, and progress, promoting transparency and accountability within the organization. By tracking task status, performance metrics, and audit trails, organizations can hold individuals accountable for their actions and ensure compliance with established processes and standards.
Implementing workflow management systems
To harness the benefits, organizations must implement robust systems and strategies tailored to their specific needs and requirements.
1. Software selection
The first step in implementing a workflow management system involves selecting the best workflow management software solution that aligns with the organization's objectives and workflows. This process typically comprises assessing the organization's requirements, evaluating available options, and selecting a solution that offers the desired features, scalability, and integration capabilities.
2. Customization
Once a workflow management system is selected, it needs to be customized to fit the organization's unique workflows and processes. This may involve configuring workflow templates, defining task dependencies, setting up automated triggers, and integrating with existing systems and applications.
3. Training
Effective training and onboarding are essential to ensure successful adoption and utilization of the workflow management system. Organizations should provide comprehensive training programs to educate users on system functionalities, best practices, and workflow procedures. Additionally, ongoing support and guidance should be offered to address user questions, troubleshoot issues, and facilitate continuous improvement.
Best practices for effective workflow management
To optimize workflow management processes and maximize efficiency, organizations should adhere to best practices and principles.
1. Documentation
Detailed documentation of processes, procedures, workflows, and project management is essential for maintaining consistency, clarity, and repeatability. Organizations should document workflow templates, task instructions, and standard operating procedures to ensure that team members have access to relevant information and guidelines.
2. Reviews and updates
Regular evaluation and optimization of workflows and project management are essential for identifying inefficiencies, addressing bottlenecks, and adapting to changing business requirements. Organizations should conduct periodic reviews of workflows, solicit feedback from stakeholders, and implement necessary updates and improvements to enhance performance and effectiveness.
3. Integration
Seamless integration with other systems and applications is essential for facilitating data exchange, interoperability, and managing workflows. Organizations should leverage integration capabilities to connect the workflow management tool with existing tools, databases, and platforms, enabling streamlined information flow and enhanced collaboration across the organization.
Managing workflow management using low-code
Low-code workflow management platforms are increasingly favored by organizations aiming to simplify workflow design and automation without heavy reliance on coding. These platforms provide user-friendly visual interfaces and drag-and-drop features, empowering users to create, modify, and implement workflows with ease, even if they lack advanced technical skills.
By eliminating the need for extensive coding knowledge, low-code solutions expedite the development process, enabling organizations to adapt to changing requirements and optimize their operational efficiency swiftly. Moreover, these platforms are versatile workflow management tools and ensure data security and compliance with regulatory standards while offering flexibility and control over the workflow environment.
Future trends
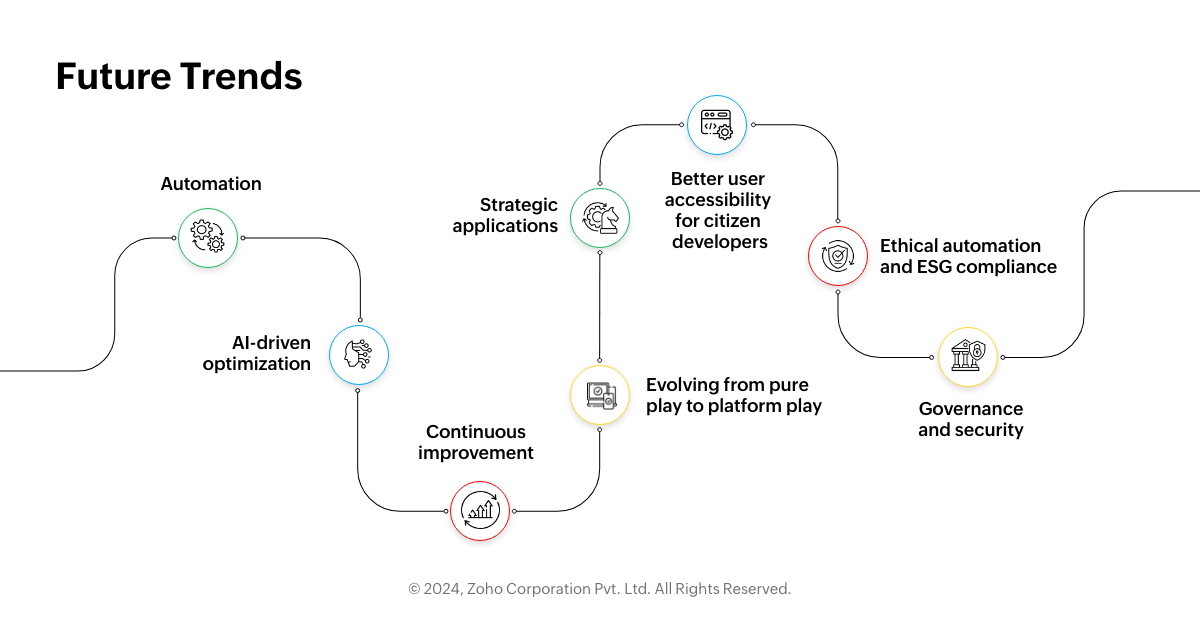
1. Automation
The future of workflow management system is heavily influenced by automation technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) and AI. These advancements are expected to revolutionize the execution of tasks—data entry, document approval, customer inquiries handling, inventory management, or any other action required to move the process forward—within workflows by automating repetitive processes.
By deploying RPA and AI, organizations can streamline operations, reduce human error, and allocate human resources to more strategic and creative tasks, ultimately boosting productivity and efficiency in project management tools.
2. AI-driven optimization
The integration of AI-driven analytics and optimization algorithms is sure to redefine workflow practices. Through sophisticated data analysis, AI can uncover valuable insights from workflow data, enabling organizations to identify inefficiencies, predict potential bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation.
By employing AI-driven optimization, organizations can continuously refine their workflows, adapt to changing demands, and stay ahead of the curve in rapidly evolving business processes.
3. Continuous improvement
The future of this management process will be shaped by methodologies that learn, evolve, and adapt continuously. These methodologies emphasize the systematic identification and elimination of waste, streamlining processes, and fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
By embracing these methodologies, organizations can drive efficiency gains, enhance quality, and remain competitive in an ever-changing marketplace, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
4. Evolving from pure play to platform play
The workflow management software method is shifting from stand-alone tools to comprehensive platforms. These platforms are designed to integrate with other business systems seamlessly, facilitating smooth data flow, end-to-end process management, and cross-functional collaboration.
By transitioning to platform play—the strategic move towards adopting integrated platforms that offer a wide range of functionalities beyond traditional stand-alone tools—organizations can achieve enhanced efficiency and agility in managing their workflows while harnessing the synergies of interconnected systems.
5. Strategic applications
Workflow automation is no longer confined to routine tasks; it is extending its reach to strategic domains like customer experience enhancement, supply chain optimization, and regulatory compliance.
Organizations are strategically deploying workflow automation to address specific business processes, gain competitive advantages, and drive innovation across various dimensions of their operations.
6. Better user accessibility for citizen developers
The democratization of automation tools is empowering non-technical users, known as citizen developers, with improved access to automation capabilities. Low-code and no-code platforms enable these individuals to create customized workflows without relying heavily on IT teams.
This accessibility fosters innovation, accelerates time-to-market, and enhances organizational agility by empowering employees at all levels to contribute to process optimization and automation initiatives.
7. Ethical automation and ESG compliance
With automation pervading various aspects of business operations, ethical considerations are taking center stage. Organizations are increasingly prioritizing responsible automation practices to ensure fairness, transparency, and compliance with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
By incorporating ethical principles into automation initiatives, businesses can uphold their commitment to ethical conduct, mitigate risks, and maintain stakeholder trust in an increasingly automated environment.
8. Governance and security
The widespread adoption of workflow automation necessitates robust governance frameworks to uphold data privacy, security, and compliance standards. Organizations are investing in secure automation practices and risk management strategies to safeguard sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance.
By prioritizing governance and security in their automation initiatives, businesses can mitigate potential risks, build resilience against cyber threats, and preserve the integrity of their workflow processes, thereby fostering trust among stakeholders and ensuring sustained success.
Get started with workflow automation using ManageEngine AppCreator
If you're looking to upgrade your workflow management processes efficiently, consider evaluating ManageEngine AppCreator as your workflow management tool. Harness the simplicity of low-code with ManageEngine AppCreator, transforming your workflow effortlessly. With its user-friendly drag-and-drop application development interfaces, AppCreator empowers stakeholders to streamline processes without requiring advanced coding skills.
By utilizing low-code capabilities, organizations can speed up the creation of tailored workflows, enhancing efficiency and adaptability across operations. The ManageEngine AppCreator platform offers a plethora of features for workflow automated processes and management, allowing you to streamline and manage workflows with ease.
This on-premise platform is a game-changer, providing a suite of tools that are adapted to your needs and designed to automate, optimize, and streamline workflows, including automated workflows, across all business sectors. AppCreator's user-friendly interface and customizable workflows give you the power to increase efficiency, promote teamwork, and boost productivity. Whether you're managing customer inquiries, automating approval workflows, or maximizing resource allocation, AppCreator has everything you need as your workflow management tool to achieve your goals. With advanced features and capabilities, this platform will help your business achieve smooth operations and superior outcomes across all functions.
So why wait? Don't hesitate—seize the opportunity to take control of your workflows today with ManageEngine AppCreator as your workflow management tool and propel your business toward success!



